In C++, data types are declarations for variables. This determines the type and size of data associated with variables. For example,
int age = 13;
Here, age is a variable of type int. Meaning, the variable can only store integers of either 2 or 4 bytes.
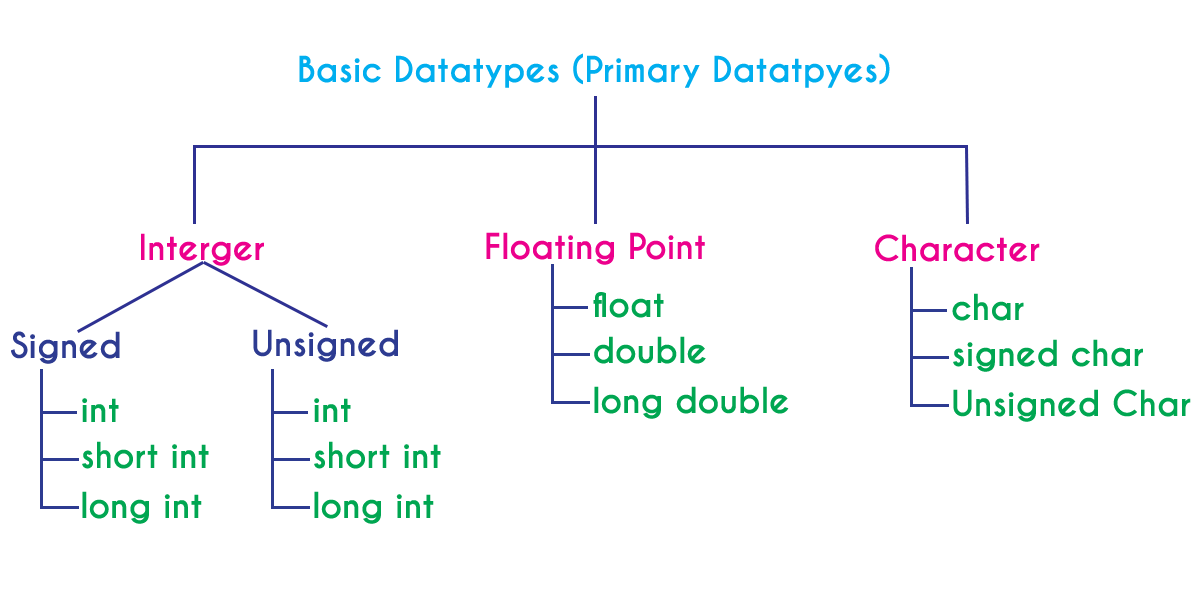
Fundamental Data Types
The table below shows the fundamental data types, their meaning, and their sizes (in bytes):
| Data Type | Meaning | Size (in Bytes) |
|---|---|---|
int | Integer | 2 or 4 |
float | Floating-point | 4 |
double | Double Floating-point | 8 |
char | Character | 1 |
wchar_t | Wide Character | 2 |
bool | Boolean | 1 |
void | Empty | 0 |
Now, let us discuss these fundamental data types in more detail.
1. int
- The
intkeyword is used to indicate integers. - Its size is usually 4 bytes. Meaning, it can store values from -2147483648 to 2147483647.
- For example,
int salary = 85000;
2. float and double
floatanddoubleare used to store floating-point numbers (decimals and exponentials).- The size of
floatis 4 bytes and the size ofdoubleis 8 bytes. Hence,doublehas two times the precision offloat. To learn more, visit C++ float and double. - For example,
float area = 64.74;
double volume = 134.64534;
As mentioned above, these two data types are also used for exponentials. For example,
double distance = 45E12 // 45E12 is equal to 45*10^12
3. char
- Keyword
charis used for characters. - Its size is 1 byte.
- Characters in C++ are enclosed inside single quotes
' '. - For example,
char test = 'h';
Note: In C++, an integer value is stored in a char variable rather than the character itself. To learn more, visit C++ characters.
4. wchar_t
- Wide character
wchar_tis similar to thechardata type, except its size is 2 bytes instead of 1. - It is used to represent characters that require more memory to represent them than a single
char. - For example,
wchar_t test = L'ם' // storing Hebrew character;
Notice the letter L before the quotation marks.
Note: There are also two other fixed-size character types char16_t and char32_t introduced in C++11.
5. bool
- The
booldata type has one of two possible values:trueorfalse. - Booleans are used in conditional statements and loops (which we will learn in later chapters).
- For example,
bool cond = false;
6. void
- The
voidkeyword indicates an absence of data. It means "nothing" or "no value". - We will use void when we learn about functions and pointers.
Note: We cannot declare variables of the void type.
Type Modifiers
We can further modify some of the fundamental data types by using type modifiers. There are 4 type modifiers in C++. They are:
signedunsignedshortlong
We can modify the following data types with the above modifiers:
intdoublechar
Modified Data Types List
| Data Type | Size (in Bytes) | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
signed int | 4 | used for integers (equivalent to int) |
unsigned int | 4 | can only store positive integers |
short | 2 | used for small integers (range -32768 to 32767) |
long | at least 4 | used for large integers (equivalent to long int) |
unsigned long | 4 | used for large positive integers or 0 (equivalent to unsigned long int) |
long long | 8 | used for very large integers (equivalent to long long int). |
unsigned long long | 8 | used for very large positive integers or 0 (equivalent to unsigned long long int) |
long double | 8 | used for large floating-point numbers |
signed char | 1 | used for characters (guaranteed range -127 to 127) |
unsigned char | 1 | used for characters (range 0 to 255) |
Let's see a few examples.
long b = 4523232;
long int c = 2345342;
long double d = 233434.56343;
short d = 3434233; // Error! out of range
unsigned int a = -5; // Error! can only store positive numbers or 0
Derived Data Types
Data types that are derived from fundamental data types are derived types. For example: arrays, pointers, function types, structures, etc.
We will learn about these derived data types in later tutorials.




No comments:
Post a Comment