In computer programming, loops are used to repeat a block of code.
For example, let's say we want to show a message 100 times. Then instead of writing the print statement 100 times, we can use a loop.
That was just a simple example; we can achieve much more efficiency and sophistication in our programs by making effective use of loops.
There are 3 types of loops in C++.
forloopwhileloopdo...whileloop
for loop
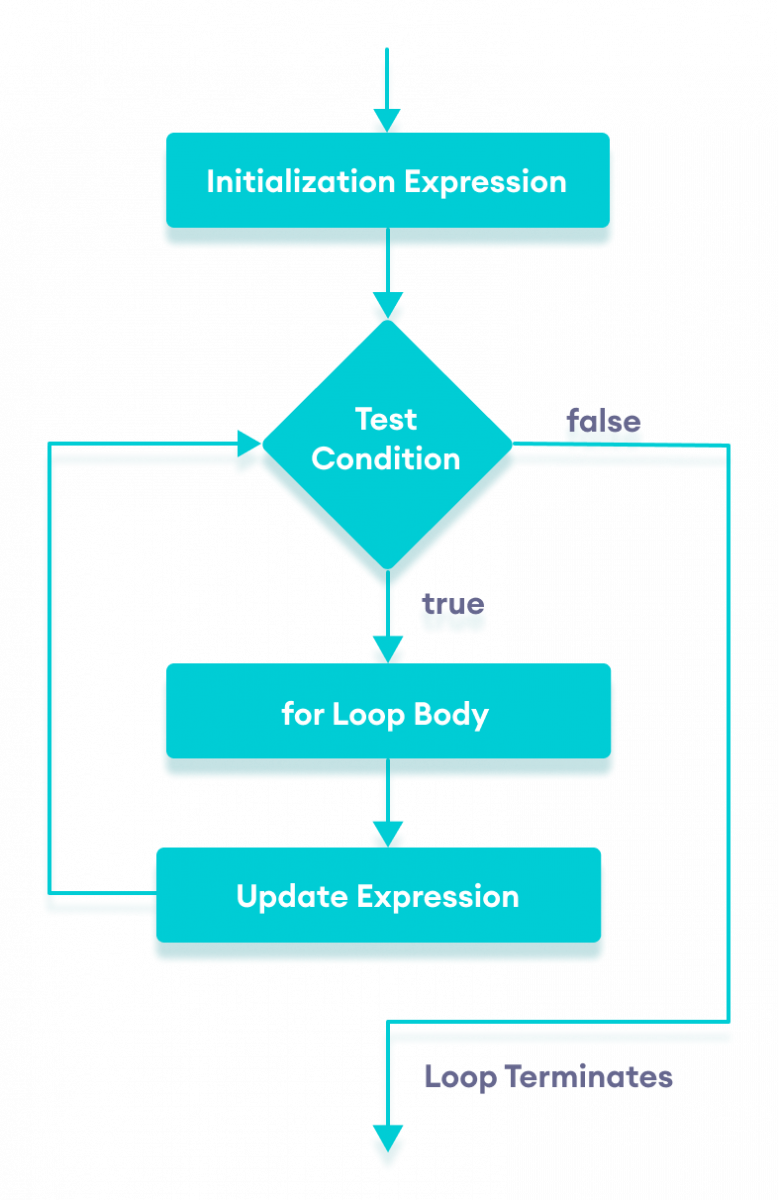
The syntax of for-loop is:
for (initialization; condition; update) {
// body of-loop
}Here,
initialization- initializes variables and is executed only oncecondition- iftrue, the body offorloop is executed
iffalse, the for loop is terminatedupdate- updates the value of initialized variables and again checks the condition
Flowchart of for Loop
Example 1: Printing Numbers From 1 to 5
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {
cout << i << " ";
}
return 0;
}Output
1 2 3 4 5
Here is how this program works
| Iteration | Variable | i <= 5 | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | i = 1 | true | 1 is printed. i is increased to 2. |
| 2nd | i = 2 | true | 2 is printed. i is increased to 3. |
| 3rd | i = 3 | true | 3 is printed. i is increased to 4. |
| 4th | i = 4 | true | 4 is printed. i is increased to 5. |
| 5th | i = 5 | true | 5 is printed. i is increased to 6. |
| 6th | i = 6 | false | The loop is terminated |
Example 2: Display a text 5 times
// C++ Program to display a text 5 times
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {
cout << "Hello World! " << endl;
}
return 0;
}Output
Hello World! Hello World! Hello World! Hello World! Hello World!
Here is how this program works
| Iteration | Variable | i <= 5 | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | i = 1 | true | Hello World! is printed and i is increased to 2. |
| 2nd | i = 2 | true | Hello World! is printed and i is increased to 3. |
| 3rd | i = 3 | true | Hello World! is printed and i is increased to 4. |
| 4th | i = 4 | true | Hello World! is printed and i is increased to 5. |
| 5th | i = 5 | true | Hello World! is printed and i is increased to 6. |
| 6th | i = 6 | false | The loop is terminated |
Example 3: Find the sum of first n Natural Numbers
// C++ program to find the sum of first n natural numbers
// positive integers such as 1,2,3,...n are known as natural numbers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num, sum;
sum = 0;
cout << "Enter a positive integer: ";
cin >> num;
for (int count = 1; count <= num; ++count) {
sum += count;
}
cout << "Sum = " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}Output
Enter a positive integer: 10 Sum = 55
In the above example, we have two variables num and sum. The sum variable is assigned with 0 and the num variable is assigned with the value provided by the user.Note that we have used a for loop.
for(int count = 1; count <= num; ++count)Here,
int count = 1: initializes the count variablecount <= num: runs the loop as long as count is less than or equal to num++count: increase the count variable by 1 in each iteration
When count becomes 11, the condition is false and sum will be equal to 0 + 1 + 2 + ... + 10.
Ranged Based for Loop
In C++11, a new range-based for loop was introduced to work with collections such as arrays and vectors. Its syntax is:
for (variable : collection) {
// body of loop
}Here, for every value in the collection, the for loop is executed and the value is assigned to the variable.
Example 4: Range Based for Loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num_array[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
for (int n : num_array) {
cout << n << " ";
}
return 0;
}Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
In the above program, we have declared and initialized an int array named num_array. It has 10 items.
Here, we have used a range-based for loop to access all the items in the array.
Infinite for loop
If the condition in a for loop is always true, it runs forever (until memory is full). For example,
// infinite for loop
for(int i = 1; i > 0; i++) {
// block of code
}In the above program, the condition is always true which will then run the code for infinite times.






No comments:
Post a Comment